Boeing XP-9
redEyes | 2003-11-08 18:37:08
조회 986 | 추천 0 | 다운로드 18
The XP-9, S/N 28-386, was Boeing's first attempt at building a single wing pursuit aircraft. The XP-9 was unsuccessful as a pursuit aircraft mainly because poor handling characteristics and the aft placement of the cockpit restricted the pilot's forward visibility.
The primary contribution of the XP-9 was the semi-monocoque (structural framework with a stressed skin) construction method which would become standard in later years.
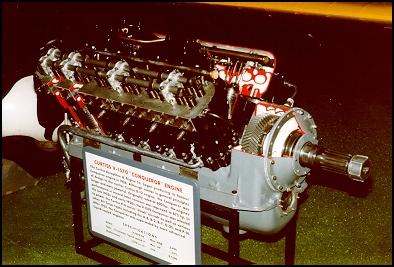
Curtiss V-1570 "Conqueror" Engine
The Curtiss Aeroplane and Engine Co. began producing its famous Conqueror engine in 1926. Although similar in general principles of design to the earlier Curtiss D-12 engine, the Conqueror was larger and more powerful. Originally rated at 600 hp., the engine's performance in several later versions was improved to 675 hp. In the late 1920s and early 1930s, the V-1570 Conqueror was selected to power the Curtiss P-6 series "Hawk" aircraft as well as various other Air Corps types including the A-8, B-2, B-7, O-25, and P-16. After 1935, the Conqueror was superseded by more advanced liquid-cooled engines.
SPECIFICATIONS:
Model: V-1570-59
Type: 12 cylinder, liquid-cooled, Vee
Displacement: 1,570 cu. in.
Maximum Horsepower: 675
Max. RPM: 2,450
Cost: $7,500
The primary contribution of the XP-9 was the semi-monocoque (structural framework with a stressed skin) construction method which would become standard in later years.
Curtiss V-1570 "Conqueror" Engine
The Curtiss Aeroplane and Engine Co. began producing its famous Conqueror engine in 1926. Although similar in general principles of design to the earlier Curtiss D-12 engine, the Conqueror was larger and more powerful. Originally rated at 600 hp., the engine's performance in several later versions was improved to 675 hp. In the late 1920s and early 1930s, the V-1570 Conqueror was selected to power the Curtiss P-6 series "Hawk" aircraft as well as various other Air Corps types including the A-8, B-2, B-7, O-25, and P-16. After 1935, the Conqueror was superseded by more advanced liquid-cooled engines.
SPECIFICATIONS:
Model: V-1570-59
Type: 12 cylinder, liquid-cooled, Vee
Displacement: 1,570 cu. in.
Maximum Horsepower: 675
Max. RPM: 2,450
Cost: $7,500








댓글 [0]